Skin cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer worldwide, affecting people of all ages, genders, and skin types. Despite its prevalence, many individuals remain unaware of crucial facts about this disease, its causes, and how to prevent it. Understanding the key facts about skin cancer can empower people to take preventive measures, recognize warning signs early, and seek timely medical care. Here are some essential skin cancer facts everyone should know.
Skin Cancer Is Common, But Preventable
Skin cancer is more common than many other cancers combined. According to health statistics, millions of new cases are diagnosed each year worldwide. However, the good news is that a large portion of skin cancer cases are preventable. Most skin cancers result from excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources such as tanning beds. Protecting your skin from UV exposure through sunscreen, protective clothing, and regular shade can significantly reduce the risk of developing skin cancer.
Types of Skin Cancer
Not all skin cancers are the same. There are three main types that everyone should be aware of:
-
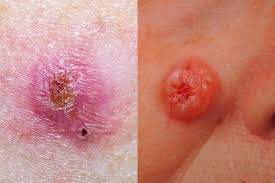
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) – This is the most common type of skin cancer. It usually appears as a small, shiny bump or patch on sun-exposed areas like the face, neck, or arms. BCC grows slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body, but early treatment is important to prevent tissue damage.
-
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) – SCC is the second most common type. It often appears as a firm, red nodule or a scaly patch that may crust or bleed. While it is generally treatable, SCC can sometimes spread if left untreated, making early detection critical.
-
Melanoma – Melanoma is less common but far more dangerous than BCC or SCC. It develops in the pigment-producing cells of the skin and can spread rapidly to other organs. Early diagnosis is vital, as melanoma can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Early Detection Saves Lives
One of the most important skin cancer facts is that early detection drastically improves survival rates. Regular self-examinations can help identify suspicious moles, spots, or lesions before they develop into serious problems. Key warning signs include changes in size, shape, or color of moles, new growths on the skin, or sores that do not heal. Anyone noticing these changes should consult a qualified skin cancer doctor immediately.
Medical professionals often use the “ABCDE” rule to evaluate potential melanomas:
-
A – Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other
-
B – Border: Irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined edges
-
C – Color: Varied shades of brown, black, or other colors
-
D – Diameter: Larger than 6 mm, about the size of a pencil eraser
-
E – Evolving: Any changes in size, shape, or color over time
Risk Factors You Should Know
Several factors increase the risk of developing skin cancer. Prolonged UV exposure, fair skin, a history of sunburns, and frequent use of tanning beds are significant contributors. Genetics also play a role; having a family history of skin cancer can make individuals more susceptible. Age and weakened immune systems can further increase the likelihood of developing the disease. Awareness of these risk factors can help people take proactive steps toward prevention and early detection.
Importance of Professional Care
While self-examination is critical, professional evaluation by a skin cancer doctor is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Doctors use specialized tools such as dermoscopy to examine suspicious lesions and may perform biopsies to confirm the presence of cancer. Early consultation ensures that treatment options are selected based on the type, stage, and location of the cancer, improving outcomes and reducing complications.
Modern Treatment Options
Treatment for skin cancer varies depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common treatments include:
-
Surgical removal – Removing cancerous tissue to prevent spread
-
Cryotherapy – Freezing abnormal cells
-
Radiation therapy – Using targeted radiation to kill cancer cells
-
Topical medications – Applied directly to affected areas for superficial cancers
-
Immunotherapy and targeted therapy – For advanced or metastatic cases
Advancements in medical technology and research have made skin cancer highly treatable when detected early. Patients who follow their doctor’s guidance and attend regular check-ups often experience excellent outcomes.
Prevention Is Better Than Cure
Prevention is a critical aspect of managing skin cancer risk. Simple measures such as applying sunscreen with broad-spectrum protection, wearing protective clothing, avoiding peak sun hours, and staying away from tanning beds can reduce the chances of developing skin cancer. Additionally, educating family members and children about sun safety can instill lifelong habits that protect skin health.
Key Takeaways
Understanding the facts about skin cancer can save lives. Here are the most important points to remember:
-
Skin cancer is common but largely preventable.
-
Early detection is crucial for effective treatment.
-
Know the types: BCC, SCC, and melanoma.
-
Recognize warning signs using the ABCDE rule.
-
Seek professional evaluation from a qualified skin cancer doctor.
-
Protect your skin from UV exposure and adopt preventive measures.
Conclusion
Skin cancer is a serious health concern, but it is manageable with awareness, prevention, and timely medical care. By staying informed about skin cancer only, understanding the risk factors, and consulting a skin cancer doctor, individuals can protect their skin health and improve treatment outcomes. Regular check-ups, sun-safe habits, and knowledge about early warning signs are your best defenses against this common disease. Everyone should take these facts seriously—because early action can save lives.